How to Fix Page With Redirect Issues in Google Search Console

If you encounter ‘page with redirect’ issues, there are three possible scenarios that could be causing the problem. In this article, I’ll explain each one step by step, along with techniques for successfully resolving them.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is Redirection?
Redirection is a way to send both users and search engines from one URL to another, often used when a page has moved or the URL has changed. Proper use of redirects helps maintain user experience and SEO performance.
Types of Redirects:
Most of the time, one of these two status codes will be returned when a redirection occurs:
301 Redirect (Permanent Redirect):
- Used when a page is permanently moved to a new URL.
- Passes most of the link juice (ranking power) from the old URL to the new one.
- Best for permanent URL changes or when moving to a new domain.
302 Redirect (Temporary Redirect):
- Used when a page is temporarily moved to a different URL.
- Doesn’t pass much link juice.
- Ideal for short-term changes, such as testing or when a page is under maintenance or for form submission redirects.
See if the redirect is temporary or permanent, 301 or 302. You can examine the redirect type using HTTP status tool or browser extensions such as Redirect Path.
What is a “Page with Redirect” Issue?
The “Page with Redirect” issue in Google Search Console (GSC) occurs when Googlebot encounters a URL that redirects to another page instead of directly serving the content. This can happen for several reasons related to how URLs are managed and redirected on your website. For more information, visit Google’s documentation to check out what they say about this issue.
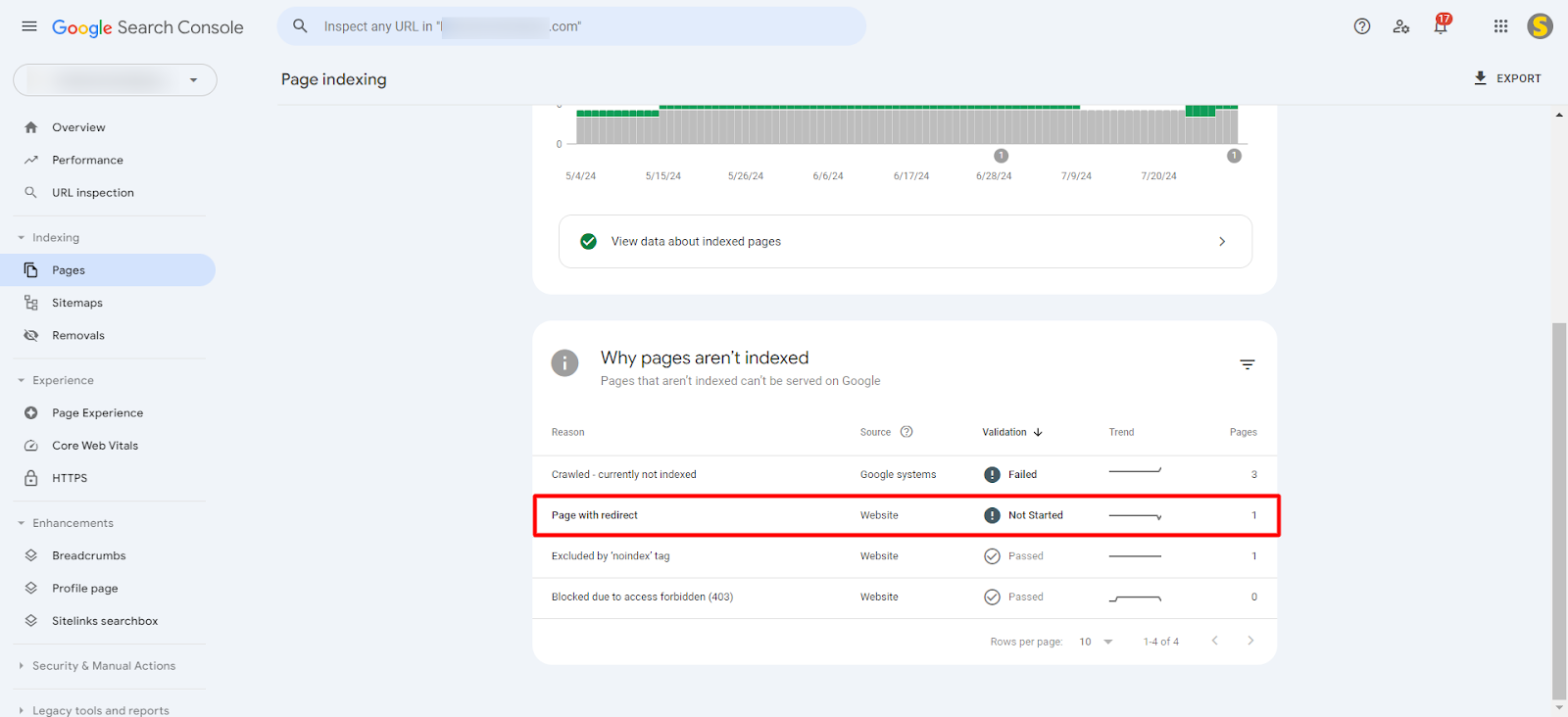
Common Factors Leading to Page with Redirect Issues:
Changing the URL Structure: When you change a page’s URL and redirect from the old URL to the new one, previously crawled URLs will be reported under the “Page with Redirect” issue.
- Domain Change: If you’ve moved to a new domain and set up domain-wide redirects (e.g., from
example.comtowww.example.com), URLs will be flagged under this issue. - Redirecting 404 Pages: Redirecting broken or 404 URLs to related pages or the homepage can cause “Page with Redirect” issues.
- Mixed Protocols or Subdomain Redirects: Internal links pointing to outdated URLs (e.g.,
http://orwww.) while the site is configured to usehttps://withoutwww.will also trigger this issue due to inconsistent internal linking.
Case Study: Fixing “Pages with Redirects” in GSC
We recently had a client who encountered an issue where 3 URLs were flagged under “Pages with Redirects” in Google Search Console. The client had deliberately changed these URLs and set up 301 redirects from the old URLs to the new ones, which is a good practice.
After reviewing the setup, we confirmed that all redirects were properly in place and verified that there were no internal links pointing to the old URLs within the website. This ensured that users and search engines were directed to the correct pages without hitting outdated links.
However, we explained to the client that if we were to remove these redirects, two things could happen:
- Search engines would lose the connection between the old and new URLs, leading to 404 errors (page not found). The search engine would then report the issue under “404 page not found,” which would impact SEO.
- If the old URLs are still indexed on other search engines or platforms, users may land on broken pages, creating a poor user experience.
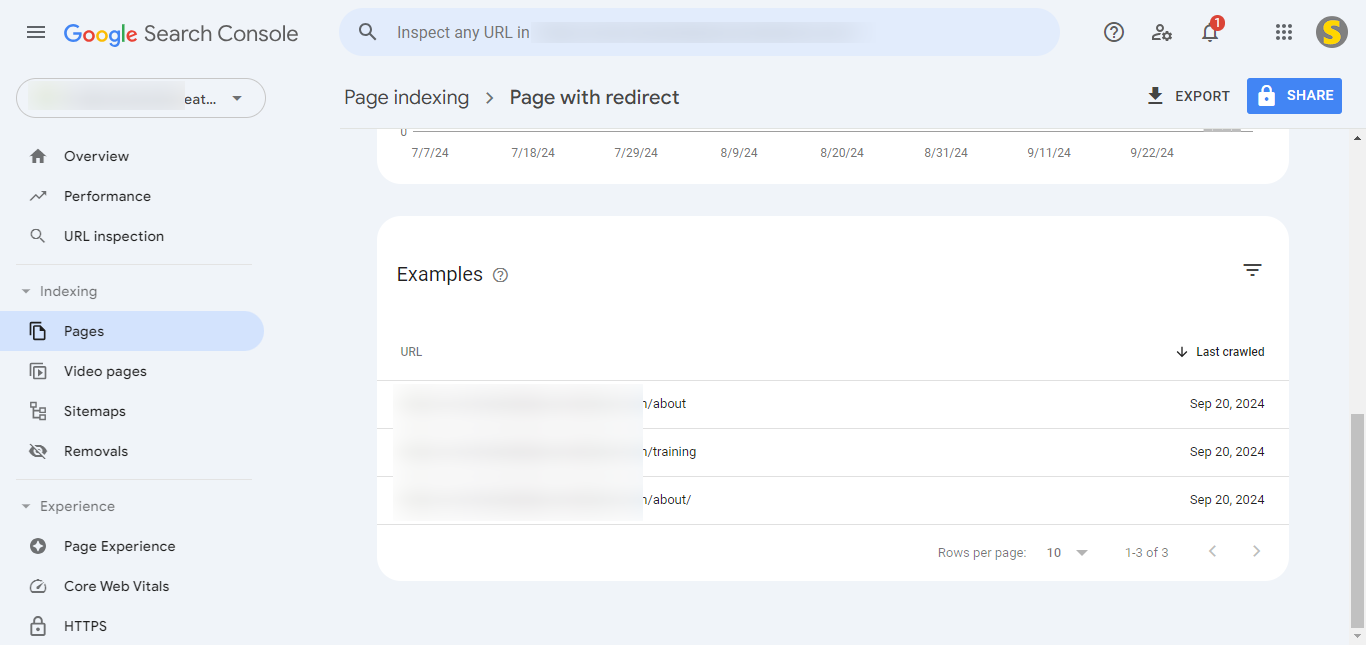
How To Fix Reported URLs in Page with Redirect
Here are the steps you can follow to effectively address the reported “Pages with Redirects” issue. Before that, it’s essential to understand the difference between submitted and non-submitted URLs:
Difference Between Submitted and Non-Submitted URLs
- Submitted URLs: These are URLs that are included in your submitted XML sitemap.
- Non-Submitted URLs: These are URLs that are not present in your submitted sitemap.
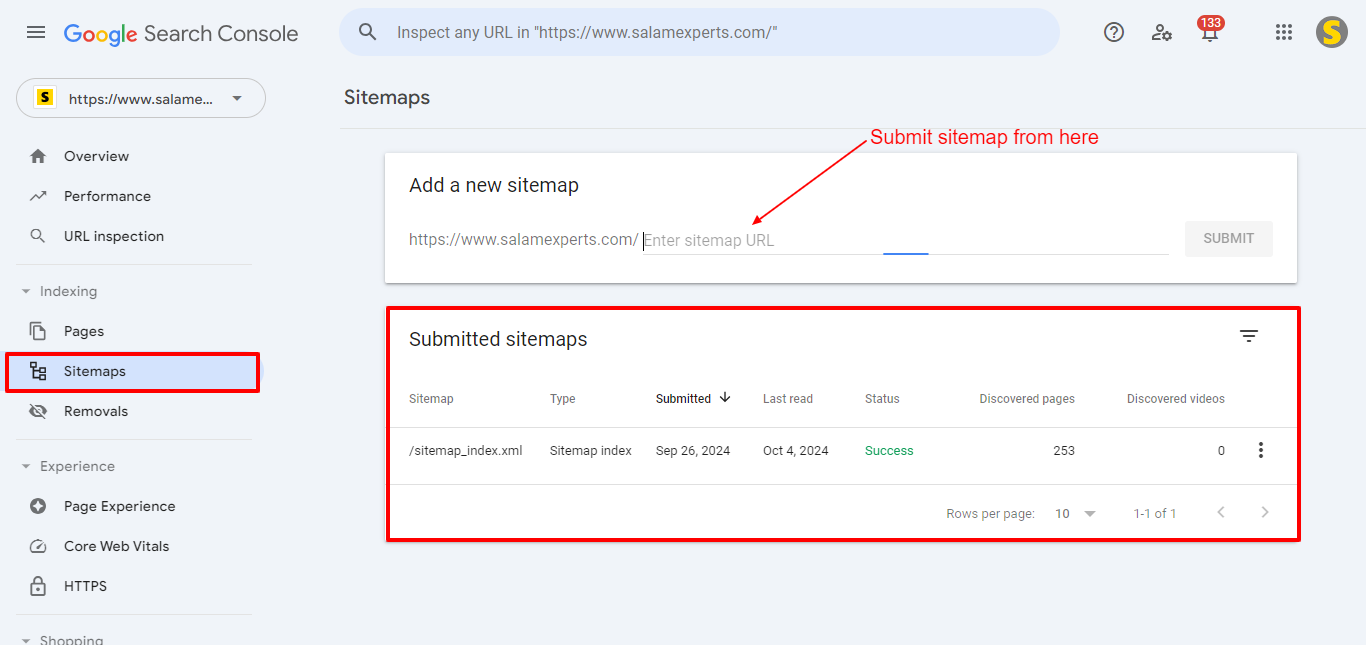
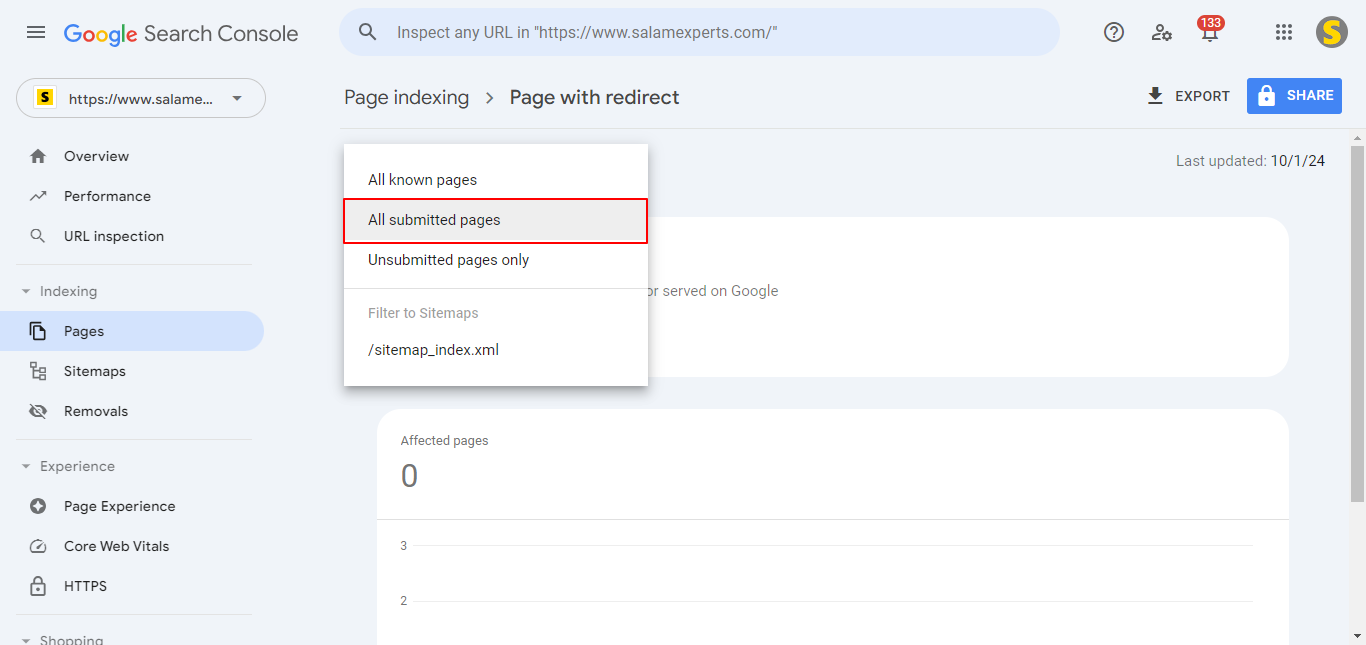
You can filter the submitted URLs by applying the filter available at the top of the GSC report, as shown in the following screenshot:
Fixing Pages with Redirects for Submitted URLs
- Fix Unintentional Redirects: After filtering the URLs, determine whether any submitted URLs should not be redirected. If a submitted URL shouldn’t be redirected, remove the redirection from that URL. Once you’ve removed the redirection, conduct a live test after inspecting the URL to ensure the page is now can be indexed.
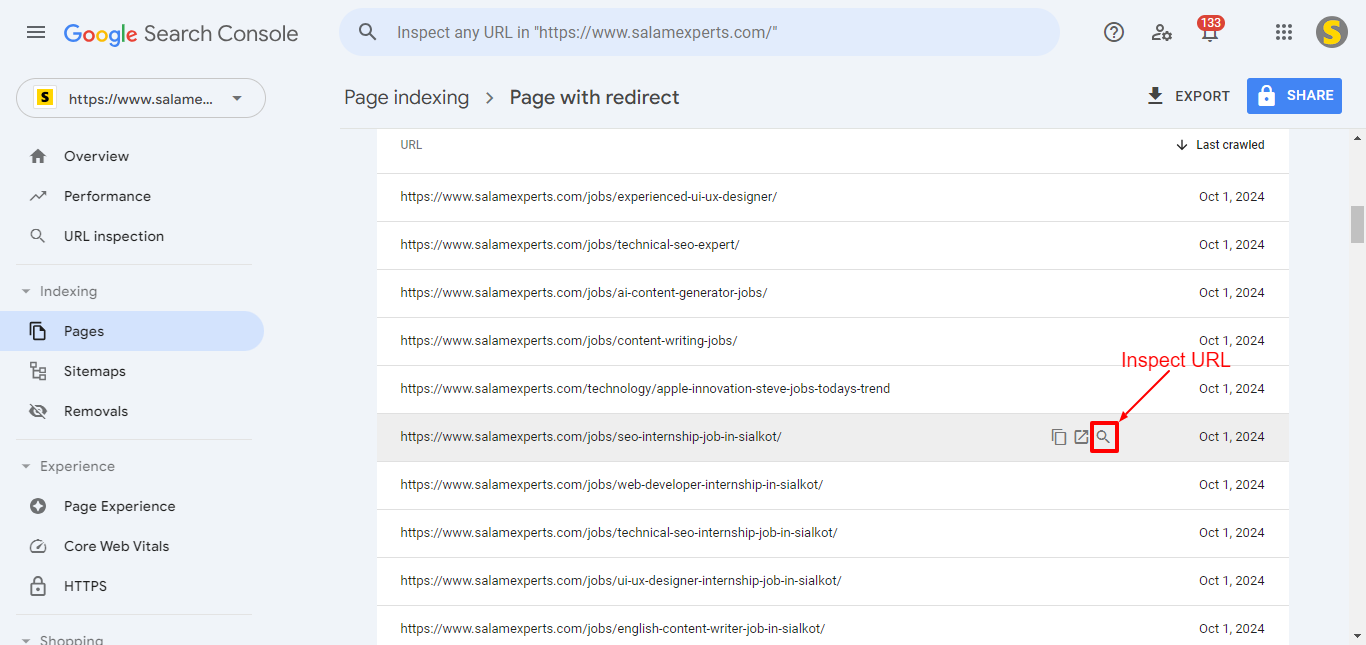
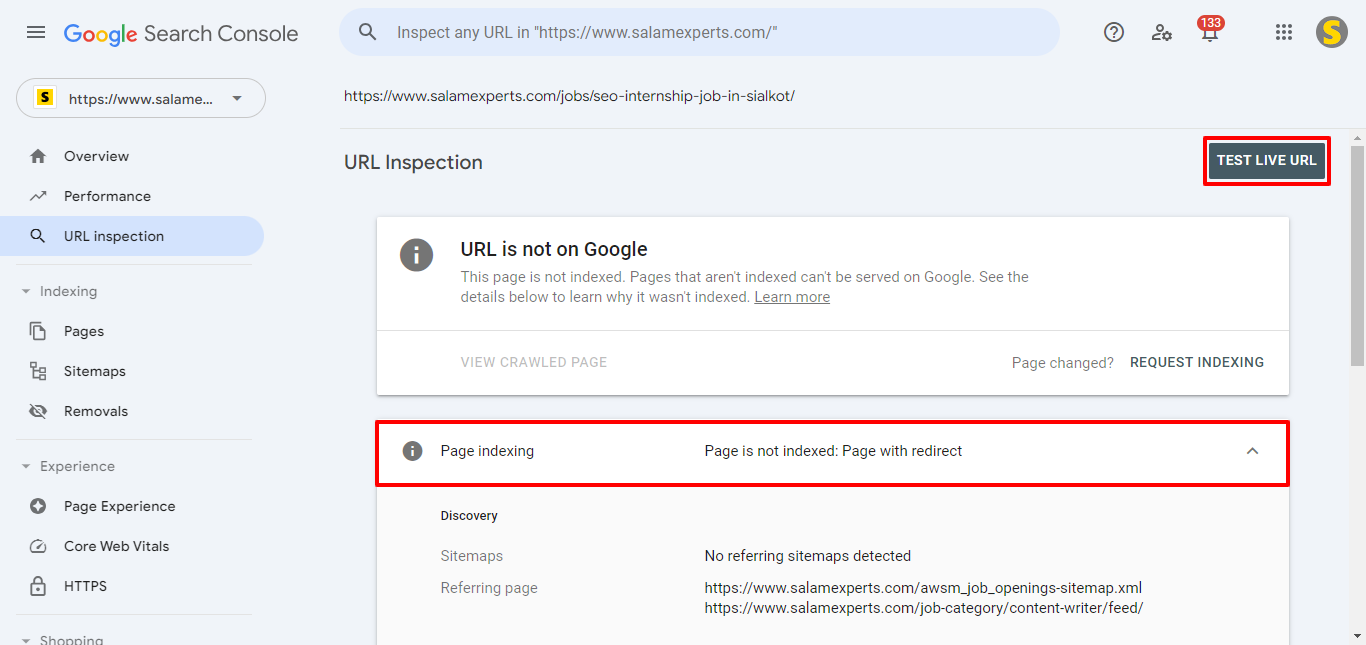
- Fix intentional Redirects: If the submitted URLs should continue redirecting, remove those redirecting URLs from the sitemap and also eliminate their internal links. To identify all internal links that may point to the 3xx URLs, use site audit tools like Ahrefs, SEMrush, or Screaming Frog.
Fixing Pages with Redirects for Non-Submitted URLs
As you know, Google identifies redirect URLs for submitted pages from the sitemap. But you might wonder where Google found the non-submitted pages with redirects. These URLs can come from various sources, including:
- Internal links within your website
- URLs that were changed, even if they don’t have internal links
- Third-party websites linking to your old URLs that are now redirecting
Correct Internal Links:
- Utilize site audit tools such as Ahrefs, SEMrush, or Screaming Frog. to identify internal links pointing to non-submitted URLs. This real-time reporting will help you locate and fix any reported 3xx URLs.
Ensure Proper Redirects:
- Check that non-submitted URLs do not redirect to 404 pages. This can lead to a negative experience for both users and Googlebot, which may affect your SEO.
Since the reported 3xx URLs should not be indexed, there is no need to worry about them or initiate validation for this issue. The redirects are intentional and serve to direct all traffic from users and bots to the correct pages.
Conclusion
Fixing “Page with Redirect” issues in Google Search Console is vital for your website’s SEO. By managing redirects effectively for both submitted and non-submitted URLs, you can ensure that users and search engines are directed to the correct pages. Intentional redirects are a valid strategy, so there’s no need for concern about validation in these cases. Following these steps will help maintain your site’s performance and user experience.

Start Building Your SEO-Optimized Website With Us!
FAQs
This issue arises when Googlebot encounters URLs that redirect to different pages instead of serving the original content. Common causes include outdated internal links, modified URLs without internal references, and third-party websites linking to your old URLs.
Non-submitted URLs are typically found through internal links, changes made to URLs, or external sites linking to your old pages. To manage these, utilize site audit tools like Ahrefs, SEMrush, or Screaming Frog to pinpoint and rectify internal links that may be leading to these redirects.
Generally, you don’t need to worry about reported 3xx URLs since they are not meant to be indexed. These intentional redirects serve to guide users and search engines to the correct pages. There’s no need to initiate validation for these issues as they won’t harm your site’s SEO.
If you identify any submitted URLs that should not have redirects, you should remove the redirection. After making these changes, conduct a live test in GSC to ensure the page is indexed correctly. If the redirects are necessary, simply remove those URLs from the sitemap and eliminate any internal links pointing to them.
To prevent redirect issues, regularly audit your site for broken or outdated links, and ensure your sitemap is always up to date. It’s crucial to maintain a clean internal linking structure, where all links point to the correct, live URLs. If you must move content, use proper 301 redirects for permanent changes to preserve SEO value.
Additionally, avoid changing URLs unnecessarily, as it can create unnecessary redirects. Keeping a consistent URL structure minimizes the chance of future redirect errors and ensures a smoother user experience.
Validation for the “Page with Redirect” issue can be initiated only if the reported URLs are no longer redirecting. If the URLs are still meant to redirect, there’s no need to start the validation, as it will fail. Google checks to ensure the reported URLs are accessible without any redirection, so if the URLs are intentionally redirecting, validation is unnecessary.
Author

We are a digital marketing agency with 17+ years of experience and a proven track record of success. We also helped businesses of all sizes grow their online presence and reach new customers. We offer a wide range of digital marketing services, including consulting, SEO, social media marketing, web design, and web development. We are the team of experienced digital marketers who are passionate about helping businesses succeed.
View all posts

